while문
while(조건식) {
조건식의 결과가 true인 동안 반복할 문장;
...
}
do {
조건식의 결과가 true인 동안 반복할 문장;
...
}while(조건식);
do ~ while문은 조건식의 결과가 처음부터 false인 경우라도 한 번은 {}에 문장을 실행함
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>while 문</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>while 문</h2>
<script>
while(true){
let num = Number(prompt('숫자를 입력하세요'));
if(num % 2 == 0){
console.log('짝수입니다. 프로그램을 종료합니다.');
break;
}
console.log('홀수입니다. 계속 진행합니다.');
break;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>


for 문
for(초기값; 조건식; 증감식){
조건식의 결과가 true인 동안 반복할 문장;
...
}
let sum = 0;
for(let i=1; i<=10; i++){
sum += i;
}
while문과의 비교
let i=1;
let sum=0;
while(i <= 10){
sum += i;
i++;
}
for문의 무한루프
for(;;){
}
break 문
switch문 또는 반복(while, for)중인 루프 내에서 사용하여 해당 문장을 완전히 종료시키고 다음에 위치한 실행문으로 이동
continue 문
반복중인 루프 내에서 사용하여 해당 루프의 나머지 부분을 건너뛰고 다음 반복문의 판단으로 넘어감
let num = 1;
while(num <= 10){
console.log(num);
num++;
if (num == 5) continue;
...
...
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>for 문</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>for 문</h2>
<script>
for(let i=1; i<=100; i++){
if(i % 3== 0){
console.log('😎');
continue;
}
console.log(i);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
문제.
원하는 숫자를 입력받아 해당 숫자의 구구단을 출력하는 문서를 만들어보자.
(단, while문, for문으로 각각 출력)
Prompt
원하는 단을 입력하세요. 4
console
4단
4 * 1 = 4
4 * 2 = 8
...
4 * 9 = 36
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>구구단</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>구구단</h2>
<script>
const dan = Number(prompt('원하는 단을 입력하세요'));
console.log(`${dan} 단`);
//while 문
let i = 1;
while(i <= 9){
console.log(`${dan} * ${i} = ${dan * i}`);
}
console.log('----------');
//for 문
for(let i=1; i<=9; i++){
console.log(`${dan} * ${i} = ${dan * i}`);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>

배열(Array)
- 이름과 인덱스로 참조되는 정렬된 값의 집합(자료구조)
- 배열을 구성하는 각각의 값을 배열요소라고 하며, 배열에서의 위치를 가리키는 숫자를 인덱스라고 함
배열 선언
let 변수명;
배열 초기화
변수명 = [요소1, 요소2, 요소3 ... ];
let arr;
arr = [100, 200, 300];
배열 생성 함수
let 변수명 = Arrray(요소1, 요소2, 요소3 ...);
배열의 접근
let arr = [100, 200, 300];
arr[0] // 100
arr[1] // 200
arr[2] // 300
자바스크립트 배열의 특징
1. 배열 요소의 타입이 고정되어 있지 않음
let arr = [1, 1.5, '김사과', true];
2. 배열 요소의 인덱스가 연속적이지 않아도 됨
let arr;
arr[0] = 1;
arr[1] = 100;
arr[4] = 10;
// index 2, 3은 undefined
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>배열 1</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>배열 1</h2>
<script>
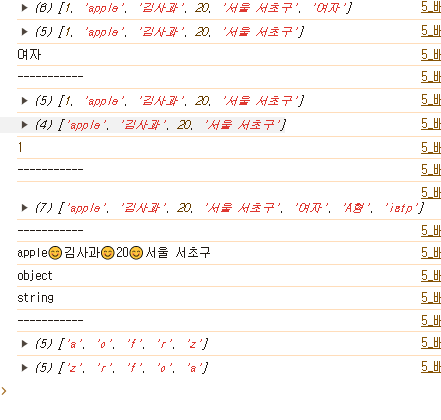
const user = [1, 'apple', '김사과', 20, '서울 서초구'];
console.log(user);
console.log(user[0]);
console.log(user[1]);
console.log(user[2]);
console.log(user[3]);
console.log(user[4]);
user[4] = '서울 강남구';
console.log(user[4]);
console.log(user.length);
console.log('------------');
for(let i=0; i<user.length; i++){
console.log(user[i]);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>배열 2</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>배열 2</h2>
<script>
const user = [1, 'apple', '김사과', 20, '서울 서초구'];
// push(): 배열의 요소를 추가
user.push('여자');
console.log(user);
// pop(): 배열의 마지막 인덱스 번호에 있는 값을 제거
let temp = user.pop();
console.log(user);
console.log(temp);
console.log('-----------');
// shift(): 배열의 첫번째 인덱스 번호에 있는 값을 제거
console.log(user);
temp = user.shift();
console.log(user);
console.log(temp);
console.log('-----------');
// concat(): 두 배열의 요소를 합침
const profile = ['여자', 'A형', 'istp'];
result = user.concat(profile);
console.log(result);
console.log('-----------');
// join(): 배열 요소 사이에 원하는 문자를 삽입
result = user.join('😊');
console.log(result);
console.log(typeof(user));
console.log(typeof(result));
console.log('-----------');
const arr = ['a', 'z', 'c', 'f', 'r'];
// sort(): 배열의 요소를 오름차순
arr.sort();
console.log(arr);
// reverse() 배열을 역순으로 재배치
arr.reverse(); // 역순 -> 내림차순
console.log(arr);
</script>
</body>
</html>
배열을 이용한 반복
for in 문
변수에 배열의 인덱스 또는 객체의 key가 저장되며 반복
const arr = [10, 20, 30];
const user = {userid: 'apple', name: '김사과', age: 20};
예)
for(let i in arr){
... // i: 0, 1, 2 (i에는 인덱스 번호가 저장)
}
for(let i in user){
... // i: userid, name, age (i에는 키가 저장)
}
for of 문
변수에 배열의 value 저장되며 반복
예)
for(let v of arr){
... // v: 10, 20, 30
}
forEach문
배열에서만 사용 가능하며 요소의 개수만큼 반복
변수명.forEach(function(변수1, 변수2, 변수3){
...
});
변수1: value가 저장
변수2: index가 저장
변수3: 모든 배열요소가 저장
* 변수2, 변수3은 생략 가능
예)
const arr = [10, 20, 30];
arr.forEach(function(v, i, a){
console.log(v); // 10, 20, 30
console.log(i); // 0, 1, 2
console.log(a); // [10, 20, 30], [10, 20, 30], [10, 20, 30]
})
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>배열 3</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>배열 3</h2>
<script>
const userArr = [1, 'apple', '김사과', 20, '서울 서초구'];
const userObj = {userid: 'apple', name: '김사과', age: 20};
// for in 배열
for(let i in userArr) {
console.log(`i: ${i}, userArr[${i}]: ${userArr[i]}`);
}
console.log('-----------');
// for in 객체
for(let i in userObj){
console.log(`i: ${i}, userObj[${i}]: ${userObj[i]}`);
}
console.log('-----------');
// for of 객체
for(let v of userArr){
console.log(`v:${v}`);
}
console.log('-----------');
// for of 객체
// Uncaught TypeError: userObj is not iterable
// for(let v of userObj){
// console.log(`v:${v}`);
// }
console.log('-----------');
userArr.forEach(function(v, i, arr){
console.log(`v:${v}, i:${i}, arr:${arr}`);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
사용자 정의 함수(function)
- 하나의 특별한 목적의 작업을 수행하도록 설계된 독립적인 블록
- 필요할 때마다 호출하여 해당 작업을 반복 수행할 수 있음
- 코드를 재활용하기 위한 목적
1. 함수 선언식
function 함수명(매개변수1, 매개변수2 ..){
함수가 호출되었을 때 실행할 문장;
...
return 값;
}
2. 함수 표현식
const 변수명 = function(매개변수1, 매개변수2, ..){
함수가 호출되었을 때 실행할 문장;
...
return 값;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>함수</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>함수</h2>
<script>
function func1(){
console.log('func1() 호출!');
}
func1();
func1();
console.log('----------');
function func2(num){
console.log(`전달받은 매개변수의 값: ${num}`);
}
func2(10);
func1('apple');
func2(true);
func2();
console.log('----------');
function func3(start, end){
let sum = 0;
for(let i= start; i<=end; i++){
sum += i;
}
console.log(`${start}부터 ${end}까지의 총합: ${sum}`);
}
func3(1, 100);
func3(1);
console.log('----------');
function func4(){
return '🎁';
}
func4();
console.log(func4());
const presents = func4();
console.log(presents);
console.log('----------');
</script>
</body>
</html>
3. 디폴트 매개변수
- 매개변수의 값을 설정하는 것
- 매개변수의 값을 정하지 않으면 기본값을 변수에 저장
function 함수명(매개변수1=값1, 매개변수2=값2, ...){
함수가 호출되었을 때 실행할 문장;
...
return 값;
}
4. 나머지 매개변수
- 생략 접두사(...)를 사용하여 특정 위치의 인수부터 마지막 인수까지 한번에 지정할 수 있음
function 함수명(매개변수1, ...매개변수2){
...
return 값;
}
함수명(값1, 값2, 값3, 값4);
매개변수1: 값1
매개변수2: 값2, 값3, 값4
function func5(num1=1, num2=1){
console.log(`num1의 값: ${num1}, num2의 값: ${num2}`);
console.log(`${num1} * ${num2} = ${num1*num2}`)
}
func5(10, 3);
func5(10);
func5();
console.log('----------');
function func6(...x){
console.log(`x의 값: ${x}`);
console.log(`x의 타입: ${typeof(x)}`);
for(i in x){
console.log(`i의 값: ${i}, x[${i}]: ${x[i]}`);
}
}
func6(30, 50, 80, 100, 40);
func6(50, 80);
// 보너스 !!
(function(){
console.log('함수를 만들고 바로 호출하기!');
})();
// func7();
// 함수 표현식
const func7 = function() {
console.log('func7() 호출!');
}
func7();

호이스팅(hoisting)
- 인터프리터가 변수와 함수의 메모리 공간을 선언 전에 미리 할당하는 것
- var로 선언한 변수의 경우 호이스팅 시 undefined로 변수를 초기화
- let과 const로 선언한 변수의 경우 호이스팅 시 변수를 초기화하지 않음
화살표 함수
- function 키워드를 사용하여 함수를 만드는 것보다 간단하게 표현
- 화살표 함수는 항상 익명
- return은 생략하며 모든 화살표 함수는 return 형
매개변수가 없는 경우
const 변수명 = function() {
...
}
const 변수명 = () => {
...
}
const 변수명 = () => 문장;
매개변수가 있는 경우
const 변수명 = 매개변수1 => {
...
}
const 변수명 = (매개변수1, 매개변수2 ..) => {
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>화살표 함수</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>화살표 함수</h2>
<script>
const func1 = () => console.log('안녕하세요! 자바스크립트!');
func1();
console.log('--------');
const func2 = x => x * x;
const result = func2(10);
console.log(`10의 제곱: ${result}`);
const func3 = (x, y) => {
let sum = 0;
for(let i=x; i<=y; i++){
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
const total = func3(1,100);
console.log(`1부터 100까지의 합: ${total}`);
let age = Number(prompt('나이를 입력하세요'));
const isAdult = (age > 19) ? () => console.log('성인입니다!') : () => console.log('미성년입니다!');
isAdult();
</script>
</body>
</html>
객체(Object)
하나의 주제를 가지고 관련있는 프로퍼티(Property)를 가지고 있는 집합
프로퍼티(Property)
- 이름과 값으로 구성된 정렬되지 않은 집합
- 프로퍼티는 함수도 저장할 수 있음 -> 프로퍼티 메서드
객체를 생성하는 방법
1. 리터럴 표기법
const 변수명 = {
프로퍼티명1: 값1,
프로퍼티명2: 값2,
...
프로퍼티명n:function() {
...
}
}
2. 생성자를 이용
- 객체를 만드는 함수
- new 연산자를 사용하여 객체를 생성하고 초기화할 수 있음
- 같은 형태의 객체를 여러개 생성할 때 유리
function 함수명(매개변수1, 매개변수2 ..){
this.프로퍼티1 = 값1;
this.프로퍼티2 = 값2;
...
this.프로퍼티n = function(){
...
}
}
const 변수1 = new 함수명(값1, 값2, ..);
const 변수2 = new 함수명(값1, 값2, ..);
3. 클래스를 이용
- ECMA Script6에 추가된 객체 생성 방법
- 내부적으로 생성자를 이용한 객체 생성 방법과 동일하게 작동
const 클래스명 = class {
constructor(매개변수1, 매개변수2, ...) {
this.프로퍼티1 = 값1;
this.프로퍼티2 = 값2;
...
}
메소드명(매개변수1, 매개변수2, ..){
...
}
}
const 변수명1 = new 클래스명(값1, 값2, ...);
const 변수명2 = new 클래스명(값1, 값2, ...);
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>객체 만들기</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>객체 만들기</h2>
<script>
//리터럴 표기법
const Rucy = {
name: '루시',
age: 14,
color: 'white',
birthday : '20091210',
getBirthday: function(){
return this.birthday;
}
}
console.log(Rucy.name);
console.log(Rucy.age);
console.log(Rucy.color);
console.log(Rucy.getBirthday);
console.log(Rucy.getBirthday());
console.log('-------------');
for(let i in Rucy){
console.log(`i:${i}, Rucy[${i}]: ${Rucy[i]}`);
}
console.log('-------------');
// 생성자를 이용한 객체
function Dog(name, color){
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
this.eat = function(){
return `${this.name} 사료를 먹습니다`;
}
}
const PPomi = new Dog('뽀미', '흰색');
console.log(PPomi.name);
console.log(PPomi.color);
console.log(PPomi.eat);
console.log(PPomi.eat());
console.log('-------------');
//클래스를 이용한 객체 생성
const Student = class {
constructor(name, hp, age){
this.name = name;
this.hp = hp;
this.age =age;
}
getName(){
return `이름은 ${this.name} 입니다`;
}
}
const apple = new Student('김사과', '010-1111-1111', 20);
console.log(apple.name);
console.log(apple.hp);
console.log(apple.age);
console.log(apple.getName);
console.log(apple.getName());
</script>
</body>
</html>

프로토타입(Prototype)
- 모든 객체는 프로토타입이라는 객체를 가지고 있음
- 모든 객체는 프로토타입으로부터 프로퍼티와 프로퍼티 메서드를 상속받음
- 모든 객체는 최소한 하나 이상의 다른 객체로부터 상속을 받으며 상속되는 정보를 제공하는 객체를 프로토타입이라고 함
const dog = new Dog(); // Dog.prototype, Object.prototype
상속
- 클래스 기반의 객체지향 언어와 다른
- 자바스크립트는 프로토타입 기반의 객체지향언어
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>프로토타입</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>프로토타입</h2>
<script>
function Dog(color, name, age){
this.color = color;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
const Rucy = new Dog('흰색', '루시', 14);
console.log(Rucy);
console.log(`이름: ${Rucy.name}`);
console.log(`색상: ${Rucy.name}`);
console.log(`나이: ${Rucy.name}`);
Rucy.family = '포메라니안';
Rucy.getFamily = function(){
return this.family;
}
console.log(`종: ${Rucy.family}`);
console.log(`getFamily: ${Rucy.getFamily}`);
const PPomi = new Dog('흰색', '뽀미', 6);
console.log(`이름: ${PPomi.name}`);
console.log(`색상: ${PPomi.name}`);
console.log(`나이: ${PPomi.name}`);
console.log(`종: ${PPomi.family}`);
// console.log(`getFamily: ${PPomi.getFamily}`);
Dog.prototype.owner = '김사과';
Dog.prototype.run = function(){
return this.name + ' 달립니다!';
}
console.log(`Rucy 소유자 : ${Rucy.owner}`);
console.log(`PPomi 소유자 : ${PPomi.owner}`);
console.log(`Rucy run() : ${Rucy.run()}`);
console.log(`PPomi run() : ${PPomi.run()}`);
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Math</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// min(): 가장 작은 수를 반환. 매개변수가 전달되지 않으면 Infinity를 반환
console.log(Math.min());
console.log(Math.min(1, 10, -10, 1000, 0, '-100'));
console.log(Math.min(1, 10, -10, '마이너스천', 0, '-100'));
// max(): 가장 큰 수를 반환. 매개변수가 전달되지 않으면 -Infinity를 반환
console.log(Math.max());
console.log(Math.max(1, 10, -10, 1000, 0, '-100'));
console.log(Math.max(1, 10, -10, '마이너스천', 0, '-100'));
// round(): 소수점 첫번째 자리에서 반올림하여 그 결과를 반환
console.log(Math.round(10.49));
console.log(Math.round(10.5));
console.log(Math.round(-10.5));
console.log(Math.round(-10.51));
// floor(): 소수점 첫번째 자리에서 소수점을 버림
console.log(Math.floor(10.49));
console.log(Math.floor(10.5));
console.log(Math.floor(-10.5));
console.log(Math.floor(-10.51));
// ceil(): 소수점 첫번째 자리에서 소수점을 올림
console.log(Math.ceil(10.49));
console.log(Math.ceil(10.5));
console.log(Math.ceil(-10.5));
console.log(Math.ceil(-10.51));
let num = 123.4567;
console.log(num * 100);
console.log(Math.round(num * 100));
// n번째 자리에서 반올림
console.log(Math.round(num * 100)/100);
console.log(num.toFixed(2));
// random(): 0보다 크거나 같고 1보다 작은 무작위 소수를 반환
const ram = Math.random()
console.log(ram); // 0.7395589987893729
// 0.7395589987893729
// 7.395589987893729
// 7
const number = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 10);
console.log(number);
</script>
</body>
</html>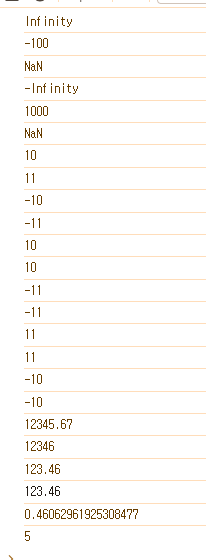
문제1.
가위, 바위, 보 게임을 만들어보자.
가위, 바위, 보 중 하나를 입력하세요. 가위
컴퓨터: 바위, 유저: 가위 -> 패
가위, 바위, 보 중 하나를 입력하세요. 바위
컴퓨터: 가위, 유저: 바위 -> 승
프로그램을 종료합니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>가위바위보 게임</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>가위바위보 게임</h2>
<script>
while(true){
const com = Math.ceil(Math.random()*3);
user = prompt('가위바위보 중 하나를 입력하세요:');
if(user == '가위') {
if(com == 1){
console.log('컴퓨터: 가위, 유저: 가위 ,비겼습니다');
}else if(com==2){
console.log('컴퓨터: 바위, 유저: 가위 ,졌습니다');
}else {
console.log('컴퓨터: 보, 유저: 가위 ,이겼습니다');
break;
}
}else if(user == '바위') {
if(com == 1){
console.log('컴퓨터: 가위, 유저: 바위 ,이겼습니다');
break;
}else if(com==2){
console.log('컴퓨터: 바위, 유저: 바위 ,비겼습니다');
}else {
console.log('컴퓨터: 보, 유저: 바위 ,졌습니다');
}
}else {
if(com == 1){
console.log('컴퓨터: 가위, 유저: 보 ,졌습니다');
}else if(com==2){
console.log('컴퓨터: 바위, 유저: 보 ,이겼습니다');
break;
}else {
console.log('컴퓨터: 보, 유저: 보 ,비겼습니다');
}
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
문제2.
로또번호를 추출하는 문서를 만들어보자.
(단, 중복된 숫자를 제거)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>로또생성기</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>로또생성기</h2>
<script>
const lotto = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0];
for(let i=0; i<lotto.length; i++){
lotto[i] = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 45);
for(let j=0; j<i; j++){
if(lotto[i] == lotto[j]){
i--;
}
}
}
console.log(lotto);
</script>
</body>
</html>'코딩 > 자바스크립트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자바스크립트, 4일차 (1) | 2024.04.18 |
|---|---|
| 자바스크립트, 3일차 (0) | 2024.04.17 |
| 자바스크립트, 1일차 (0) | 2024.04.15 |
| [JavaScript] 문자열에서 특정 문자의 개수를 세는 예 (0) | 2022.06.13 |
| [JavaScript] 문자열에서 특정 문자의 인덱스(위치)를 검색하는 예 (0) | 2022.06.13 |

